728x90
1. auto commit 모드 끄기
- 커넥션이 생성되면 바로 auto commit 모드로 세팅된다
- 즉, 각 SQL문이 완료되는 족족 commit된다. 그 다음 실행된다
- 완료 → commit → 실행
- 그래서 동시에 업데이트 하려면 auto commit 모드를 꺼야 한다
con.setAutoCommit(false);con : active connection
2. Transaction commit하기
- auto commit 모드를 끄면 commit() 명령실행 전까지 commit하지 않는다
- commit을 실행하면 현재 트랜잭션에서 모든 SQL명령들이 하나의 unit으로 반영된다
public void updateCoffeeSales(HashMap<String, Integer> salesForWeek) throws SQLException {
String updateString =
"update COFFEES set SALES = ? where COF_NAME = ?";
String updateStatement =
"update COFFEES set TOTAL = TOTAL + ? where COF_NAME = ?";
try (PreparedStatement updateSales = con.prepareStatement(updateString);
PreparedStatement updateTotal = con.prepareStatement(updateStatement))
{
con.setAutoCommit(false);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : salesForWeek.entrySet()) {
updateSales.setInt(1, e.getValue().intValue());
updateSales.setString(2, e.getKey());
updateSales.executeUpdate();
updateTotal.setInt(1, e.getValue().intValue());
updateTotal.setString(2, e.getKey());
updateTotal.executeUpdate();
con.commit();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
JDBCTutorialUtilities.printSQLException(e);
if (con != null) {
try {
System.err.print("Transaction is being rolled back");
con.rollback();
} catch (SQLException excep) {
JDBCTutorialUtilities.printSQLException(excep);
}
}
}
}- auto commit을 끄면 PrepareStatement인 updateSales과 updateTotal은 commit() 명령이 실행되는 동시에 commit된다
- 트랜잭션 내의 statement에 의한 모든 변경은 영구적이다
- Transaction 내부에서는 다음 업데이트 전까지 항상 값을 (영구)보존하고 있다는 뜻이다
- 트랜잭션 내에서 auto commit을 꺼야되는 이유는 매 SQL 구문이 완료될 때마다 여러 사람이 접근한다면 테이블 lock이 걸릴 수 있기 때문이다
3. 데이터 완결성을 보장하기 위한 Transaction Isolation사용
- 트랜잭션을 사용하는 동안 테이블 내 데이터는 완결성이 보장된다
- DBMS는 conflict를 피하기위해 lock을 사용한다
- 다른 사람이 data에 접근하는 것을 막는 대신 트랜잭션으로 접근하는 방법을 사용한다
- 왜냐면 auto commit 모드에서는 statement마다 commit되기 때문에 누구든지 접근할 수 있다
- lock이 세팅되면 트랜잭션이 commit이나 rollback할 때까지 무적상태가 된다
- 트랜잭션 isolation이 lock을 세팅한다
- 트랜잭션 모드를 변경가능
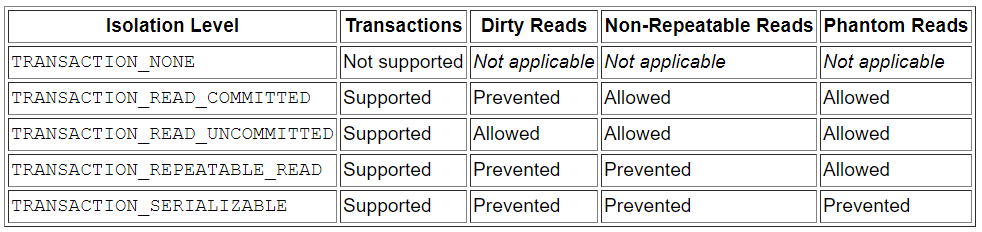
TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED
- commit 하기 전까지 접근 불가
dirty read를 허락하지 않는다- dirty read는 업데이트 되었지만 아직 commit하지 않는 값을 읽음
- 문제는 만약에 rollback된다면 이 세상에 존재하지 않는 값을 읽고 있는게 되버린다
- 참고 : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18297626/difference-between-non-repeatable-read-vs-dirty-read
non repeatable read허락- non repeatable read는 두개의 commit된 값을 읽는다
- T1이 업데이트를 하고 동시에 T2를 업데이트한 이후, T1이 값을 읽으려고하면 T1과 T2가 업데이트한 값을 읽을 수 있다
repeatable read는 자신이 트랜잭션한 내용만 읽는다- 만약 T1이 업데이트했다면 동시에 T2가 업데이트 한 내용은 무시한다
phantom reads는 하나의 트랜잭션이 다른 트랜잭션에 의해 추가/삭제된 row를 읽는다
그냥 default 사용하면 된다.
- java db : TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED
Connection.setTransactionIsolation(TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED)
Connection.getTransactionIsolation()4. SavePoint에 Rollback 세팅
- savepoint : 현재 트랜잭션에서 저장 포인트 설정
- rollback : savepoint를 아규먼트로 받음
SavePoint save = con.setSavepoint();
con.rollback(save);public void modifyPricesByPercentage(
String coffeeName,
float priceModifier,
float maximumPrice) throws SQLException {
con.setAutoCommit(false);
ResultSet rs = null;
String priceQuery = "SELECT COF_NAME, PRICE FROM COFFEES " +
"WHERE COF_NAME = ?";
String updateQuery = "UPDATE COFFEES SET PRICE = ? " +
"WHERE COF_NAME = ?";
try (PreparedStatement getPrice = con.prepareStatement(priceQuery, ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
PreparedStatement updatePrice = con.prepareStatement(updateQuery))
{
Savepoint save1 = con.setSavepoint();
getPrice.setString(1, coffeeName);
if (!getPrice.execute()) {
System.out.println("Could not find entry for coffee named " + coffeeName);
} else {
rs = getPrice.getResultSet();
rs.first();
float oldPrice = rs.getFloat("PRICE");
float newPrice = oldPrice + (oldPrice * priceModifier);
System.out.printf("Old price of %s is $%.2f%n", coffeeName, oldPrice);
System.out.printf("New price of %s is $%.2f%n", coffeeName, newPrice);
System.out.println("Performing update...");
updatePrice.setFloat(1, newPrice);
updatePrice.setString(2, coffeeName);
updatePrice.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("\nCOFFEES table after update:");
CoffeesTable.viewTable(con);
if (newPrice > maximumPrice) {
System.out.printf("The new price, $%.2f, is greater " +
"than the maximum price, $%.2f. " +
"Rolling back the transaction...%n",
newPrice, maximumPrice);
con.rollback(save1);
System.out.println("\nCOFFEES table after rollback:");
CoffeesTable.viewTable(con);
}
con.commit();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
JDBCTutorialUtilities.printSQLException(e);
} finally {
con.setAutoCommit(true);
}
}- 위의 코드는 newPrice가 maximumPrice보다 큰 경우,
con.rollback(save1)에 의해 savepoint로 돌아간다 - 그리고 커밋을 하게 되면, 롤백되었기 때문에 아무런 값도 업데이트 되지 않는다
- 그 외의 조건들을 commit을 수행하여 업데이트가 된다
5. Savepoint 삭제
- 현재 트랜잭션에서 savepoint 없애기
- savepoint 삭제 후 rollback을 시도하면 SQLException 발생
Connection.releaseSavepoint(save)6. 언제 rollback 함수를 호출할 것인가
- rollback을 실행하면 트랜잭션은 끝난다
- 그리고 업데이트 이전 값으로 돌아간다
- 여러개의 statement를 트랜잭션 내에서 실행할 때, SQLException이 발생한다면 rollback을 호출할 것이고 트랜잭션을 빠져나간다. 그리고 다음 statement를 위해 트랜잭션을 다시 실행한다
- SQLExcpetion을 누가 어디에서 rollback되었는지 알려주지 않으므로 catch문에 명시적으로 rollback을 해야 이전 commit포인트를 유추할 수 있다
정리
- 기본적으로 auto commit을 제공하고 statement 하나하나를 커밋한다
- 트랜잭션을 사용하려면 auto commit을 꺼야한다
- 트랜잭션 내부에서는 commit될 때까지 lock이 설정되고 값이 보존된다
- 트랜잭션 isolation이 lock의 범위를 설정한다
- TRANSACTION_NONE
- TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED (java 기본)
- TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
- TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
- TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE
- Savepoint로 rollback할 지점을 정할 수 있다
- statement가 여러개라면 rollback으로 트랜잭션이 끝난 이후에 새로운 트랜잭션이 시작된다
728x90



